Alibaba Cloud ECS supports creating custom images based on existing system disk snapshots. A custom image includes the operating system, as well as various software, configurations, and data installed on the ECS instance. By using a custom image, you can create ECS instances with the same environment as the original instance, enabling rapid replication of the system environment.
Steps
The following are the steps to use a snapshot to replicate the same system environment to a new server:
Creating a Custom Image
Prerequisites:
- A system disk snapshot has been created. For specific operations, see [Creating Snapshots](link to creating snapshots).
- Sensitive data in the snapshot has been deleted to avoid data security risks.
Go to the Alibaba Cloud ECS console and click “Storage & Snapshots” on the left to enter the snapshot page.
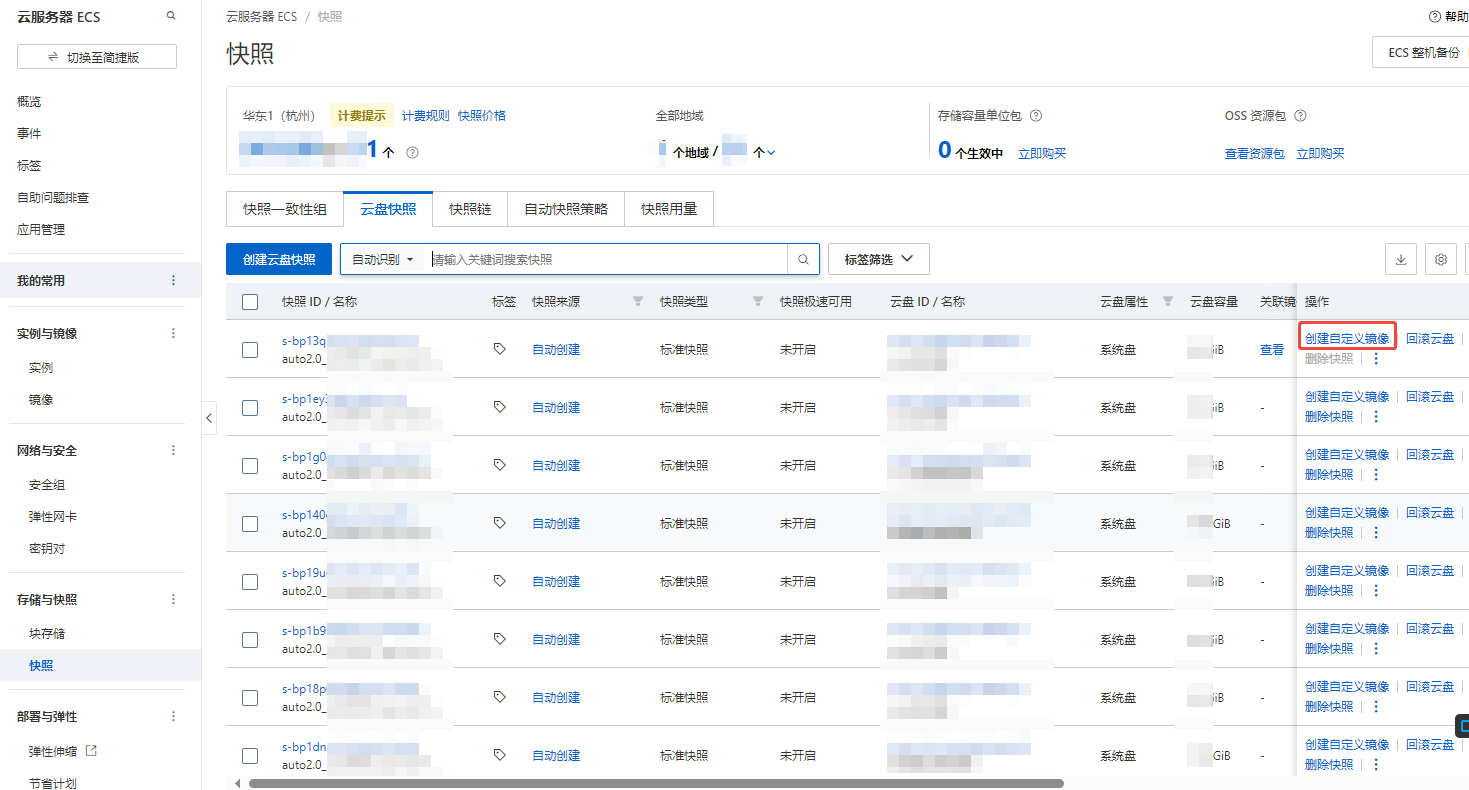
Select the snapshot for which you want to create an image, and click “Create Custom Image”. Once created, you can see it on the image page.
Using the Image
You can directly create a new server on the image page, or you can use the custom image to replace the operating system of an existing server (to replicate the system environment).
Here, we will demonstrate the latter operation. Go to the server instance page, click the “Replace” button under “Operating System”, and select a custom image to replace (it will automatically shut down to switch the image and restart).
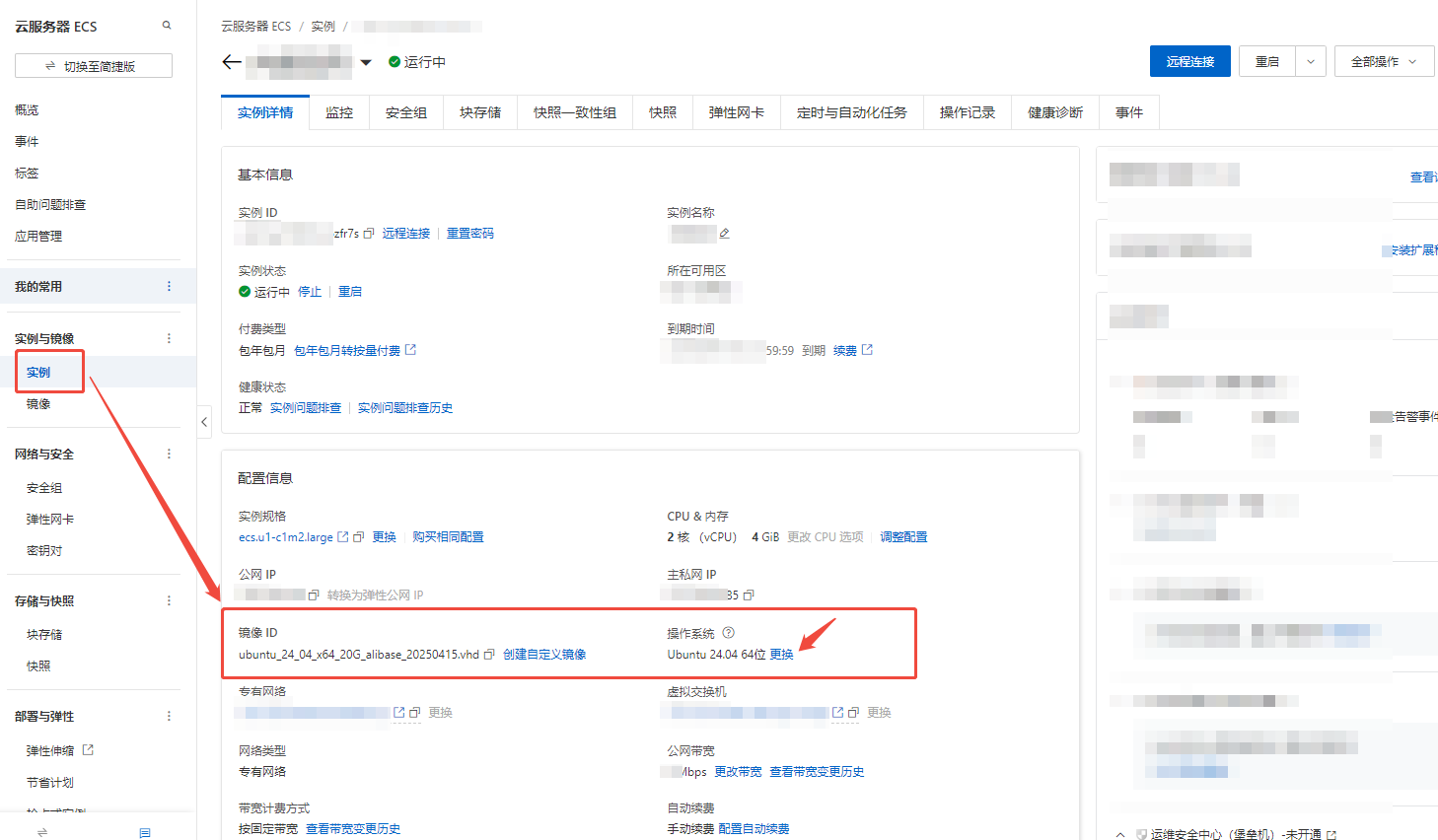
Wait for the replacement to complete.
Problem Encountered
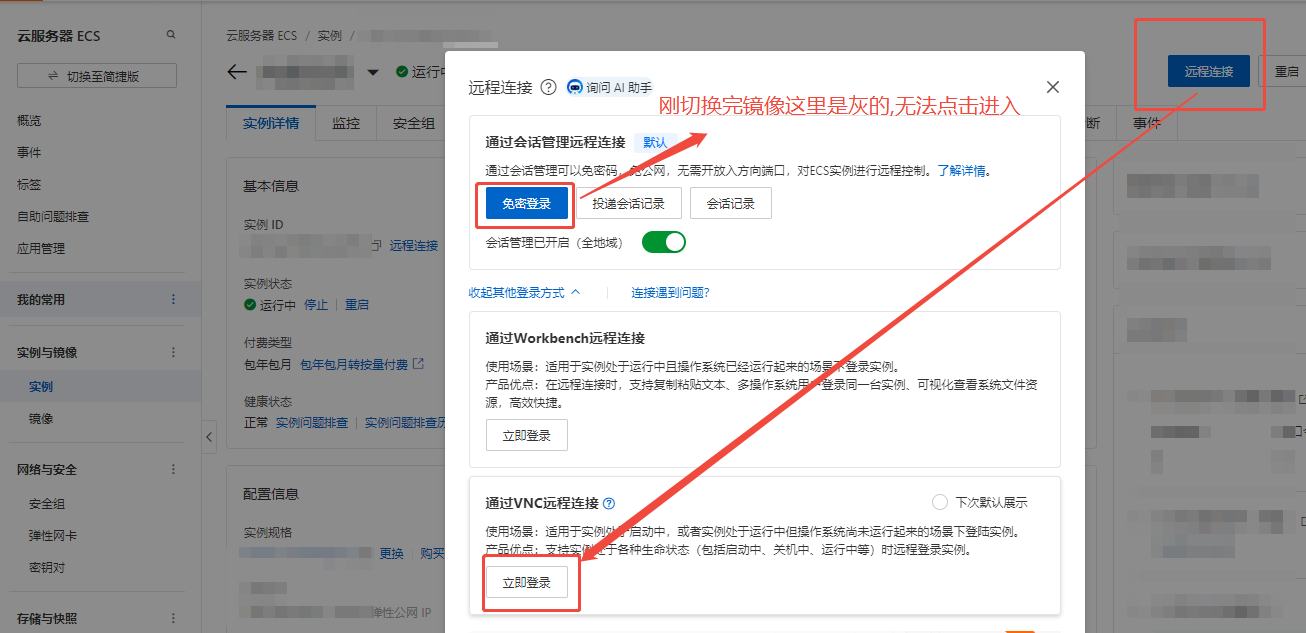
Under normal circumstances, the server should function properly after the image is replaced (such as using images provided by the cloud marketplace or official sources). However, I am using a custom image, and a problem has arisen where the server status is consistently incorrect, displaying “Operating system is starting” even after waiting for several hours. I am unable to connect to the server via SSH, and the “Password-free Connection” on the “Remote Connection” page is also grayed out and unusable, as shown in the figure:
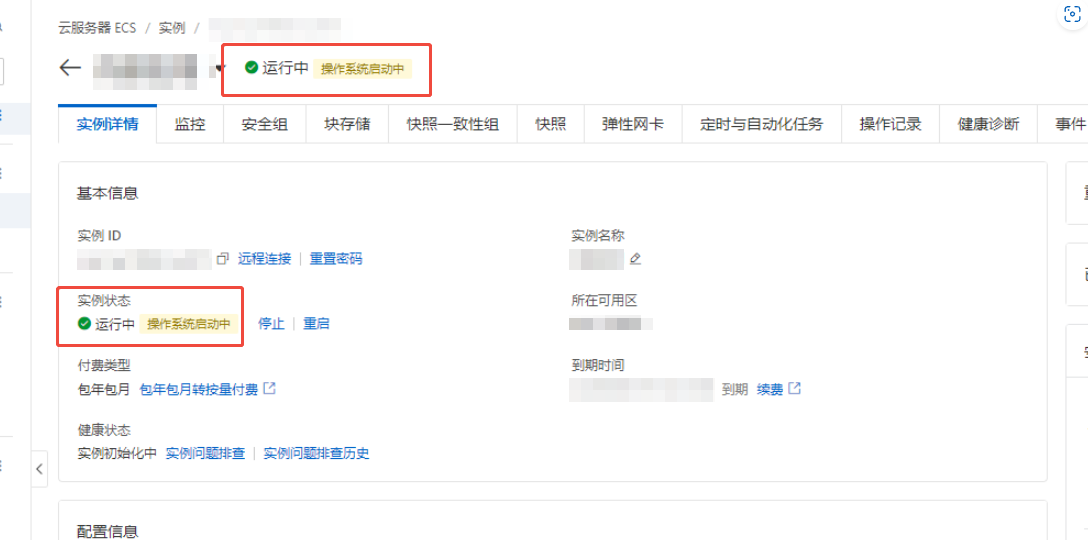
After contacting customer service, the issue was resolved. Password-free login is unavailable, but a VNC remote connection can still be established. If the password is uncertain, it can be reset on the page (at this point, the server has actually completed the image switch and finished booting, but because the custom image contains network card information from the old server, the server IP is incorrect, causing the server status to be incorrect. It is necessary to reload the network card and obtain a new IP via DHCP for normal use).
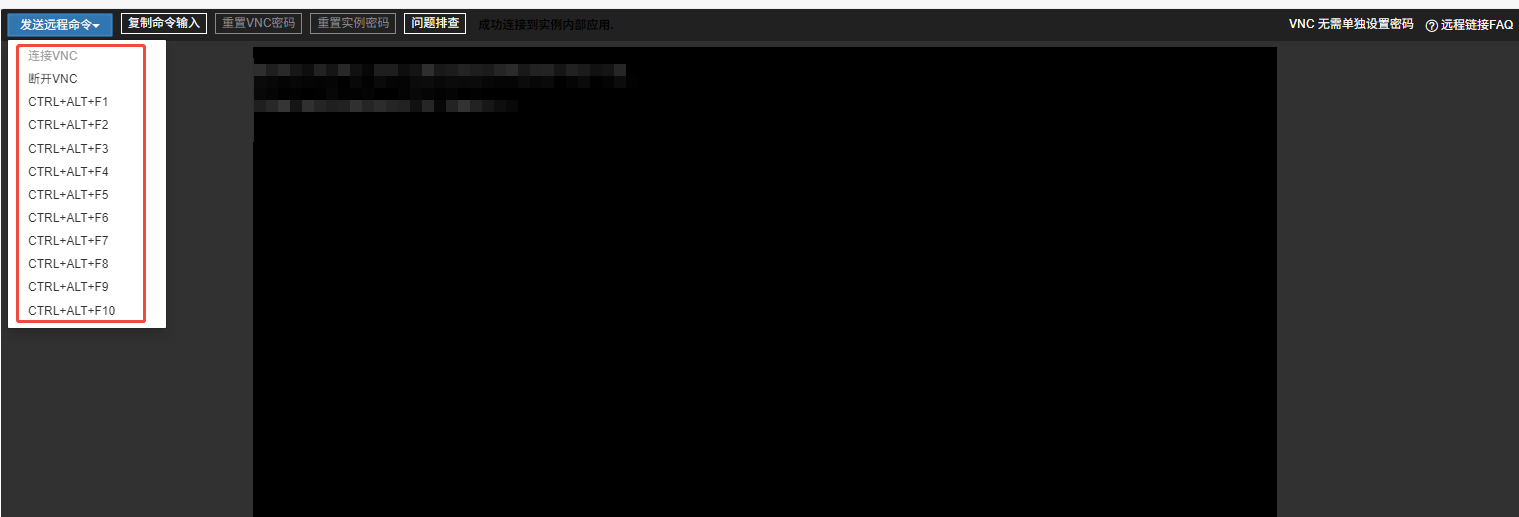
If the default connection through VNC does not display the username and password input, you need to click “Send Remote Command” in the upper left corner to switch. After switching, you can normally enter the username and password to log in.
Restarting the Network Card
Use the command dhclient:
1 | dhclient |
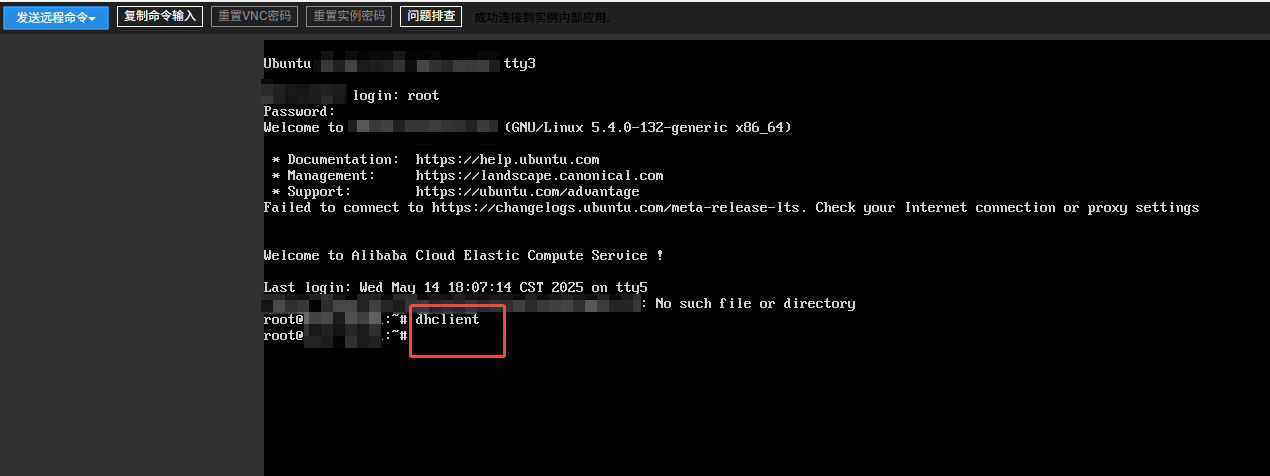
After reloading, the server status will return to normal after a while.
dhclient
dhclient is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client program.
Purpose: To automatically obtain network configuration information such as IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server from the DHCP server, simplifying network configuration and implementing dynamic IP address allocation.
Using dhclient is very simple; usually, you only need to enter the dhclient command in the terminal. However, the specific usage depends on your needs and system configuration. Here are some common usages:
Basic Usage:
Start the DHCP client and obtain an IP address:
1
sudo dhclient
This will instruct
dhclientto attempt to obtain an IP address from all available network interfaces.sudois usually required because it needs administrator privileges to modify network configurations.Specify the network interface to use:
1
sudo dhclient <interface_name>
For example, to obtain an IP address from the
eth0interface, you can use:1
sudo dhclient eth0
Common Options:
-vor--verbose: Verbose output, providing more information about the DHCP process.1
sudo dhclient -v eth0
-ror--release: Release the current IP address.1
sudo dhclient -r eth0
This will notify the DHCP server that the client is no longer using the IP address. It is usually used before closing a network connection or changing network configurations.
-dor--no-daemon: Run dhclient in the foreground, not as a daemon. This is useful for debugging.1
sudo dhclient -d eth0
-qor--quiet: Quiet mode, only displays error messages.1
sudo dhclient -q eth0
-p <port_number>: Specify the port number that dhclient listens on. Rarely needs to be modified.-lf <file_path>: Specify the path to the leases file. The leases file stores the IP address information obtained by dhclient. By default, the leases file is usually located at/var/lib/dhcp/dhclient.leasesor/var/db/dhclient.leases.
Common Usage Scenarios:
Manually obtain an IP address: When network connections have problems or after restarting network services, you can use
dhclientto manually obtain an IP address.Restart a network interface: You can use
ifdown <interface_name>to close the interface, and then useifup <interface_name>to start the interface. The system will automatically calldhclientto obtain an IP address (provided that the interface is configured for DHCP).Release and re-obtain an IP address: You can use
dhclient -r <interface_name>to release the IP address, and then usedhclient <interface_name>to re-obtain the IP address. This can solve some network problems.
Configuration File:
The configuration file for dhclient is usually located at /etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf. You can configure the behavior of dhclient in this file, such as requesting specific DHCP options, setting timeouts, etc. Usually, you do not need to modify this file unless you have specific needs.
Precautions:
- Ensure that your network interface is enabled and configured to use DHCP.
- You need to use the
sudocommand to rundhclientbecause it needs to modify network configurations. - Check the system logs (e.g.,
/var/log/syslogor/var/log/messages) to get more information about the DHCP process.
Summary:
The most commonly used commands are sudo dhclient and sudo dhclient <interface_name>. They can automatically obtain network configuration information and simplify network connection settings. If you encounter network problems, you can try using dhclient -r to release the IP address and then re-obtain it.
Reference
Summary
This article describes how to use Alibaba Cloud snapshots to quickly replicate system environments and how to solve the problem of the server always displaying “Operating system is starting” after using a custom image.
The main steps include:
- Create a custom image from a snapshot.
- Use the custom image to replace the server’s operating system.
- Connect to the server via VNC and execute the
dhclientcommand to restart the network card to resolve the incorrect server status display.